A practical, up-to-date guide to how wireless charging works today
Wireless Charging (2026 Guide)

Wireless charging has become a core charging method for modern devices. In 2026, it is no longer a novelty or convenience feature, but a mature technology built on global standards such as Qi wireless charging, Qi2, and the newer Qi2.2 specification.
This guide explains how wireless charging works, how fast and safe it really is today, how it affects battery health, and how technologies like MagSafe charging (Apple) fit into the wider wireless charging ecosystem. The goal of this page is to give clear, accurate, up-to-date information — not marketing claims.
Why This Guide Exists
Wireless charging is widely used today, but many people still have questions about how it works, whether it’s safe for batteries, and how modern standards compare to older chargers.
This guide is designed to answer those questions clearly — without unnecessary technical jargon.
Quick Summary: Wireless Charging in 2026
- Wireless charging is safe for everyday use when using Qi-certified chargers
- Qi2 improves efficiency through magnetic alignment
- Qi2.2 enables higher power levels (up to 25W on supported devices)
- MagSafe charging is Apple’s magnetic wireless charging system
- Wireless charging is suitable for desk, overnight, car, and daily top-ups
How Modern Wireless Charging Works

Wireless charging is a method of transferring electrical power without a physical cable connection. Instead of electricity flowing through a wire, energy is transferred using electromagnetic induction between a charger and a compatible device.
Most modern wireless charging is defined by the Qi standard, developed by the Wireless Power Consortium. Qi ensures that chargers and devices can communicate safely, regulate power correctly, and work across different brands.
Newer generations of the standard have improved real-world performance:
- Qi2 adds magnetic alignment for better efficiency and consistency
- Qi2.2 expands Qi2 by enabling higher power profiles, including up to 25W on supported devices
Charging begins automatically when a device is placed on a compatible charger and stops when it is removed.
Explore Real-World Wireless Charging
Want to see how modern wireless charging is used in real products?
Explore wireless charging solutions designed around today’s Qi standards.
How Wireless Charging Actually Transfers Power
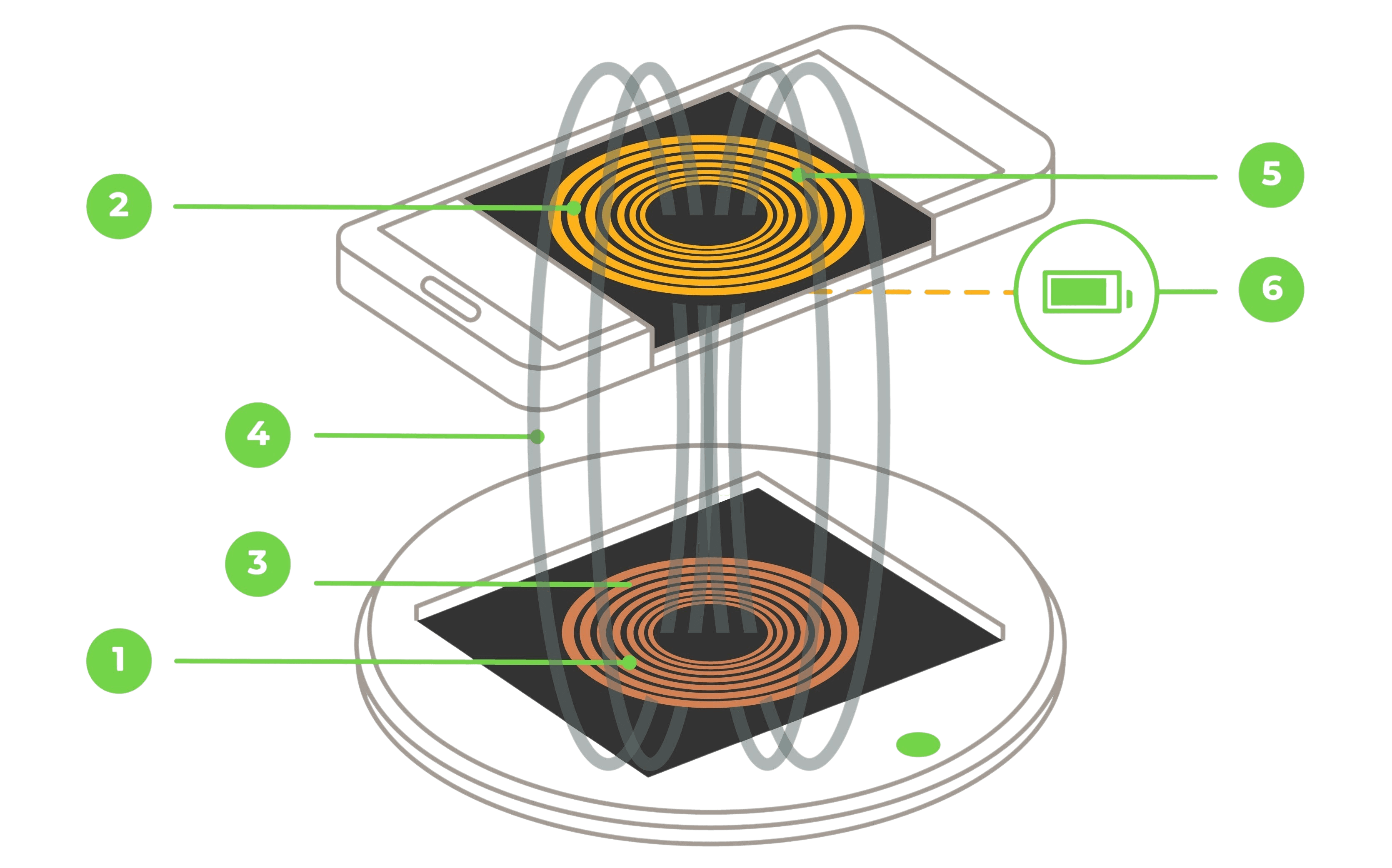
Wireless charging relies on electromagnetic induction, a technology used safely in many industries.
The charging process works as follows:
- The charger generates a controlled magnetic field
- A receiver coil inside the device detects the field
- An electrical current is induced in the receiver coil
- The current is converted into power for the battery
This process is defined and regulated by Qi, Qi2, and Qi2.2 standards to ensure safety and compatibility.
Qi2 Wireless Charging
Qi2 is a newer generation of the Qi standard that introduces magnetic alignment.
- Magnetic alignment helps:
- Ensure consistent coil positioning
- Reduce energy loss
- Improve charging stability
- Lower unnecessary heat
Qi2 does not automatically make charging faster, but it significantly improves real-world reliability and efficiency.
Qi2.2 Wireless Charging (2025–2026)
Qi2.2 builds on Qi2 by enabling higher power profiles on supported devices. This allows wireless charging to scale beyond earlier limits while maintaining safety.
Depending on device and charger support, Qi2.2 can enable wireless charging up to 25W. Not all devices use these higher power levels, but the standard ensures future compatibility.
MagSafe Charging (Apple)

MagSafe charging is Apple’s proprietary magnetic wireless charging system used on iPhones.
MagSafe uses magnetic alignment similar to Qi2, but it:
- Operates within Apple’s ecosystem
- Depends on Apple device firmware
- Is not identical to Qi2, even though concepts overlap
MagSafe chargers can be Qi-compatible, but MagSafe performance is determined by Apple device support.
View Compatible Wireless Chargers
Looking for wireless chargers built around modern standards?
Explore wireless chargers designed for everyday use, modern Qi standards, and reliable long-term charging.
How Fast Is Wireless Charging in 2026?
Is wireless charging fast enough today?
Yes.
In 2026, modern wireless charging can deliver up to 25W on supported devices, depending on:
- Charging standard (Qi, Qi2, Qi2.2)
- Device compatibility
- Charger design and power source
While wired charging can still reach higher peak speeds, wireless charging is now fast enough for:
- Desk charging
- Overnight charging
- In-car charging
- Frequent daily top-ups
For most users, wireless charging meets everyday needs.
Is Wireless Charging Safe?
Yes. Wireless charging is safe in 2026.
Modern Qi-certified wireless chargers include built-in safety systems such as
- Temperature monitoring
- Overvoltage protection
- Foreign object detection
- Smart power regulation
These features ensure safe operation during short charging sessions, long sessions, and overnight charging.
Is Wireless Charging Bad for Battery Health?
No. Wireless charging does not damage batteries when used correctly.
Modern wireless charging:
- Regulates power delivery
- Slows charging as the battery fills
- Reduces wear on physical charging ports
This aligns well with modern battery management systems used by Apple and Android devices, supporting long-term battery health.
Wireless Charging and Phone Cases

Can you use wireless charging with a phone case?
Yes.
Most wireless chargers work through standard plastic and silicone cases. MagSafe-compatible cases improve alignment on supported chargers, but removing the case is usually unnecessary.
Choosing the Right Wireless Charger
Understanding wireless charging standards helps you choose chargers that fit your daily routine.
When selecting a wireless charger, look for:
- Qi certification
- Support for modern standards
- Proper heat management
- Compatibility with your device and case
Ready to Upgrade Your Charging Setup?

Wireless charging in 2026 is efficient, safe, and practical for everyday use. Built on Qi2, Qi2.2, and MagSafe-compatible alignment, modern wireless chargers support how devices are actually used.

























































